Blockchain is a virtual infrastructure that was initially used for cryptocurrencies. The technology was designed at the outset to issue bitcoins, but today it is shaking up the financial markets as well as a number of other sectors in the economy.
 Public, transparent and secure technology
Public, transparent and secure technology
The outlook for bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies remains unsure, but the future for blockchain is definitely bright. Blockchain emerged at the same time as bitcoin in 2009 and is often described as the largest technological revolution since the internet was invented.
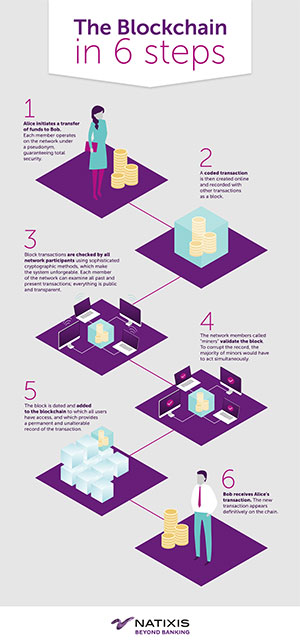
Blockchain is a bit like a large register that records all exchanges and transactions conducted between users. Time-dated entries are recorded chronologically in blocks from the first to the last transaction, and information is publicly available. In more concrete terms, this system enables users to store and send digital information transparently and securely at a low cost, with no need for a supervisory body or trusted third party. Blockchain technology is not controlled by any one individual or a financial institution, but rather by a network of computers, or network nodes as they are known, and cryptographic calculations. This allows for digital assets and other types of assets – ownership titles, shares, currencies, etc. – to be exchanged transparently. Blockchain is also very specific in that it can be distributed and shared, which means that all members in the group have an identical copy of the account ledger that records all transactions, while a cryptographic validation system means that data cannot be changed or tampered with.
This obviously carries huge advantages, particularly for banks, which are conducting an increasing number of experiments to develop innovative services based on this technology.
Strong success for private blockchains
The blockchain technology developed for bitcoin was what is known as public blockchain i.e. anyone can get involved, issue a transaction and record it in the register, as long as he/she follows the rules governing the system.
However, a number of companies in the finance, trade and insurance sectors have started to look into the potential harbored by this technology as they seek to adapt it to suit their own individual needs, leading to the development of a new concept – the private blockchain. In this case, access is reserved exclusively for certain members. Private blockchains offer most of the same advantages as the original public technology, such as guaranteed authenticity and also decentralization to a certain extent. However, they also enable financial institutions not only to control their blockchain but also to choose users and more importantly for some, ensure transaction confidentiality.
This new approach has attracted a great deal of interest well beyond the finance sector and we are beginning to see blockchain experiments on a wider scale in sectors such as retail, government service, culture (copyright management), transport, healthcare, real estate, etc.
According to a Market & Research report, the blockchain technology market could be worth as much as $7.7 billion out to 2022.
Blockchain is already a reality here at Natixis

Read the expert’s view of Frédéric Dalibard , Head of Digital at Corporate & Investment Banking at Natixis. He tells us about the strong interest in blockchain technology and its uses in the banking sector.














