We are in the throes of the digital revolution, but how about we stop to consider the environmental footprint it creates. The digital sector may well be invisible, but it has very real consequences for our environment.
So just what environmental impact does our digital use have, and how can we be more green behind our screen?
Digital pollution is the new digital ecology frontier
Many people are still unaware of the impact of digital technology on the environment, with a 2019 survey from the International Weather and Climate Forum (IWF) revealing that only 40% of survey participants in France realize the strong connection between digital and climate change.
However, it is mostly the smaller items that now use the most energy i.e. smartphones, tablets, connected objects, computers, etc.
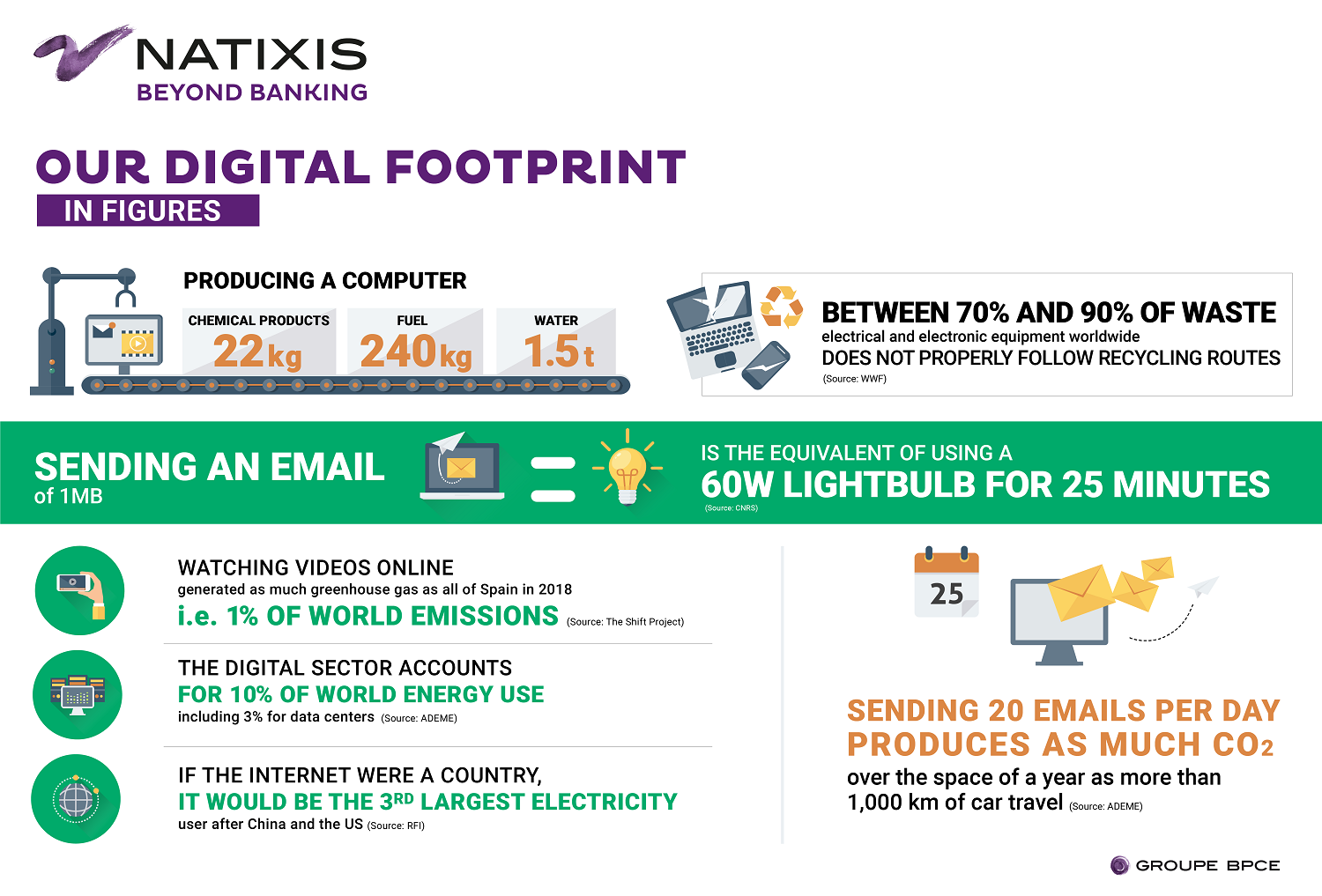
The digital sector creates several different types of pollution:
- Pollution from the production of IT hardware;
- Pollution from e-waste i.e. used electrical and electronic equipment;
- Pollution from our daily digital use.
Combining digital transformation and environmental responsibility
There are a number of ways to make our digital usage more responsible i.e. raising awareness of digital ecology, software eco-design, re-using IT equipment, re-using energy from data centers, etc.
Natixis is a signatory to the French Responsible Digital Institute’s Responsible Digital Charter (website in French only), and has taken a number of measures to tackle digital pollution and ensure responsible digital transformation. These initiatives are laid out in a roadmap with the aim of coordinating and developing our actions.
Natixis’ responsible digital strategy combines efficiency and strict management
Our initiatives are based on three key projects.
The first is “Green for IT”, which is aimed at cutting back our digital environmental footprint via responsible purchasing, optimizing our equipment rate and re-using or recycling hardware.
The second aspect is “responsible design”, which seeks to promote eco-design best practices for applications, data and hardware.
The third and last area is “IT for Green”, which explores how IT can support the environment by helping reduce travel.
Concrete examples of our responsible digital policy
Giving IT hardware a second life for charity
Natixis gifts its used laptops and tablets to the Saint Maurice Hospital school in the Paris region, providing around one hundred children with access to communications and learning tools that are tailored to their disabilities. This initiative combines charity with environmental responsibility, re-using equipment to provide cost savings for the hospital, while also avoiding e-waste.
Find out more about Natixis’ program to give its computers and tablets a second useful life (video in French only)
Natixis’ data center used to heat a swimming pool
Data centers are used to store and share computer data. They operate 24/7 and use a great deal of energy, particularly the refrigerating units required to cool the servers, which account for around a third of energy use.
However, there are ways to make for more green data centers, such as free cooling. This technique uses outside air to naturally cool rooms where servers are stored, or directly mainframe computers, thereby reducing the use of artificial cooling.
Another example of our affirmative climate action is in the Paris region, where the Val d’Europe water park pools are heated by a Natixis data center. Almost half of the heat produced by servers has been re-used each year since 2011.
Watch the video to find out more (video in French)
Digital usage and environmental responsibility at the office
Storing data, looking for information on the internet, sending or storing an email are all daily – and seemingly innocuous – actions that can actually have a major environmental impact.
Some tips to cut back your digital carbon footprint at work include:
- Clearing out your inbox: regularly empty your trash folder, and unsubscribe from newsletters you do not read.
- Hitting the sleep button on your computer: use energy-saving mode, do not leave your computer or tablet on standby, etc.
- Curbing the number of emails you send: keep the number of attachments and email recipients to a minimum.
- Optimizing your internet searches: use URLs, add your most-used pages to your favorites and use your browser history when you want to reopen a page.
- Deleting any documents you no longer need: do not keep documents that are no longer useful, such as old versions of your files.
- Opting for collaborative tools to share documents rather than sending them by email.
More tips for cutting back your environmental digital footprint (document in French)






